Understanding When a Headache Might Be More Than Just a Migraine
Headache Might Be More Than Just a Migraine
If you’ve been experiencing persistent headaches that last longer than usual, it’s natural to wonder if there’s an underlying cause. While migraines are common, continuous or unusual headaches might raise concerns about a potential brain tumour. Understanding the differences between these two conditions is crucial in avoiding unnecessary stress and seeking the right medical attention.
If you’re dealing with unexplained headaches, consulting a top neuro specialist in hyderabad can provide clarity and ensure an accurate diagnosis. Both migraines and brain tumour-related headaches have distinct causes and symptoms. Recognizing the key differences can help you make informed decisions about your health. Let’s explore how to differentiate between a migraine and a brain tumour.
What Are Migraines?
Migraines are severe headaches often accompanied by nausea, light sensitivity, and in some cases, temporary vision loss. These headaches can last for hours or even days. Many people wonder whether migraines are linked to cancer, but there is no connection between the two.
Migraines typically affect one side of the head and worsen with physical activity. Common triggers include stress, hormonal fluctuations, specific foods, and environmental factors. Unlike headaches caused by brain tumours, migraines do not lead to neurological issues like memory loss or seizures.

Can a Headache Be a Sign of a Brain Tumour?
A brain tumour is an abnormal mass of cells growing in the brain. While not all brain tumours cause headaches, many patients report experiencing chronic, unexplained head pain. Unlike migraines, headaches associated with brain tumours tend to worsen over time and are usually accompanied by other symptoms.
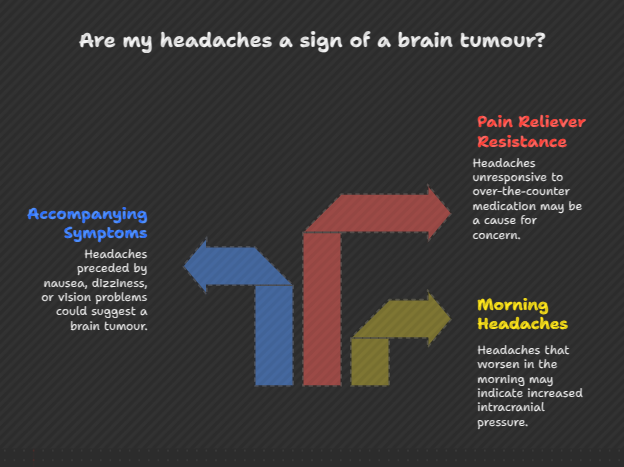
Some key characteristics of brain tumour-related headaches include:
- Worse in the morning
- Preceded by nausea, dizziness, or vision problems
- Unresponsive to over-the-counter pain relievers
While migraines are triggered by external factors, brain tumour headaches result from increased pressure inside the skull. If you’re experiencing frequent, unexplained headaches, seeking medical advice is essential.
How to Differentiate Between a Brain Tumour and a Migraine
Here are the primary differences between migraine headaches and headaches caused by brain tumours:
FactorMigraineBrain TumourPain LocationTypically affects one side of the headDeep, persistent pain that worsens over timePatternTriggered by specific factors like stress, diet, or environmentOccurs randomly and gradually increases in intensityOther SymptomsNausea, light sensitivity, temporary vision disturbancesMemory loss, speech difficulties, vision impairment
Headaches caused by brain tumours tend to intensify steadily, whereas migraines follow a more predictable pattern. If headaches are disrupting your daily life, consulting a neurologist is recommended.

Symptoms That Require Immediate Medical Attention
While most headaches are harmless, certain symptoms warrant urgent medical evaluation. If you’ve had a headache lasting over a month, a brain tumour could be a possibility, especially if the pain is progressively worsening.
Other warning signs include:
- Recurring headaches that don’t improve with treatment
- Seizures or confusion
- Nausea and vomiting without any other illness
- Speech difficulties or sudden vision changes
Ignoring these symptoms can delay diagnosis and treatment. If you experience any of these issues, see a doctor without delay.

Does Stress Cause Brain Tumours?
A common concern is whether stress can lead to brain tumours. The answer is no — stress does not cause brain tumours. However, chronic stress can negatively impact brain health and contribute to migraines.
Stress triggers inflammation, which can worsen headaches and neurological symptoms. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, proper sleep, and exercise can help prevent migraines. However, if you suspect your headaches are not stress-related, seeking medical advice is the best course of action.

Diagnosing the Cause of Your Headache
Proper diagnosis is crucial to distinguish between migraines and brain tumour-related headaches. Doctors use various tests, including:
- Medical history review: Evaluating symptoms and past health conditions
- Imaging tests: CT scans and MRIs to detect abnormalities
- Neurological exams: Assessing memory, reflexes, and motor functions
If you frequently experience headaches along with other concerning symptoms, a consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Realted Blogs:
Trigeminal Neuralgia: Can It Cause Neck and Shoulder Pain?
When is Back Pain a Sign of a Serious Spine Condition?
Advanced Neurological Care in India
Neurologists evaluate each case individually and recommend tailored treatments, which may include medication, radiation therapy, or surgery. With medical advancements, effective treatment options are available for those diagnosed with brain tumours.
When to Seek Expert Care
While migraines can be debilitating, understanding the difference between migraines and brain tumour headaches is crucial. If your headache pattern changes, worsens, or comes with other concerning symptoms, seeking professional medical advice is the best step forward.
For an accurate diagnosis and expert treatment, trust a qualified specialist. Dr. Raveesh Sunkara is an experienced neurologist offering comprehensive care for patients experiencing chronic headaches or other neurological issues. Don’t take chances with your health — schedule an appointment today and get expert medical attention.
📅 Book Your Consultation Now!
FAQs
Can a migraine turn into a brain tumour?
No, migraines do not develop into brain tumours. They have distinct causes and are not linked to cancer.
What type of headache does a brain tumour cause?
Brain tumour headaches are persistent, worsen over time, and may be accompanied by neurological symptoms like vision problems or memory loss.
How long do headaches from a brain tumour last?
Brain tumour headaches are chronic and typically do not improve with regular painkillers.
What are the early signs of brain cancer?
Early symptoms may include ongoing headaches, seizures, memory issues, and personality changes.
When should I see a doctor for recurring headaches?
If you’ve had headaches for several weeks, they’re getting worse, or they come with neurological symptoms, visit a doctor as soon as possible.
